














|
The method of passing down genes in animals is what makes inheritance so interesting and confusing at the same time. To simplify the process of inheritance, we will follow one gene through the process and show how it gets passed on.
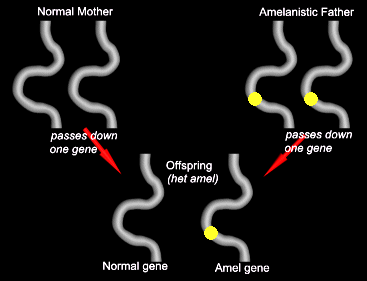
First, we’ll take an amelanistic cornsnake and a normal (homozygous) cornsnake and breed them together.
|
Notice that both parents are homozygous. In this case, the mother will always give offspring the normal gene, and the father will always give the amel gene.
All of the offspring will be normal-looking, but will have one copy of the mutated gene. They will be “het for amel.”
|
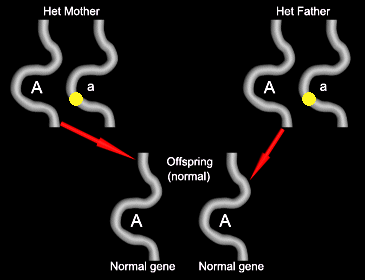
If we cross two of these offspring together, there are four different combinations that can happen. Each of these has an equal chance of happening. In the following pictures, the dominant normal gene is represented by A, and the recessive mutant gene is represented by a.
|
Some of the offspring will get both copies of the normal gene. These will appear normal.
|
|
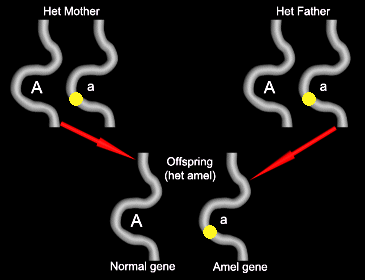
Some of the offspring will get the mutant gene from the father. These will appear normal, and will be “het for amel.”
|
|
|
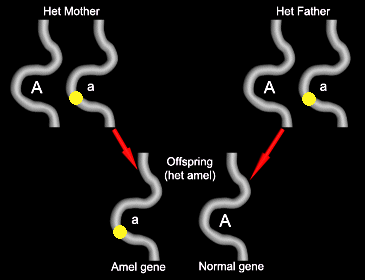
Some of the offspring will get the mutant gene from the mother. These will appear normal, and will be “het for amel.”
|
|
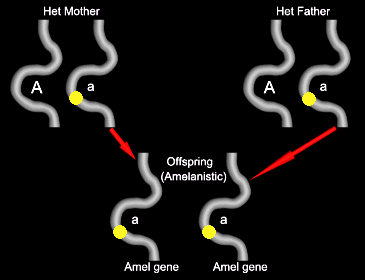
Some of the offspring will get the mutant gene from the father, and the mutant gene from the mother. These will be amelanistic.
|
|
Since these 4 outcomes are all equally likely, the clutches from this type of mating will tend to be 25% amelanistic, and 75% normal. Of the normal-looking offspring, 2 out of 3 will be “het for amel.” But you can’t tell which ones are the hets, so these are referred to as “possible het” animals. In this case, they are 66% likely to be het for amelanism. They are often sold as “66% het.”



 |
Get more details with the book Genetics For Herpers!
It's 84 pages of illustrated genetics fun! |

|
Now Free in PDF format!
|
 |
|
 |
|

 Privacy Policy Privacy Policy
 Hide Ads Hide Ads
|

















